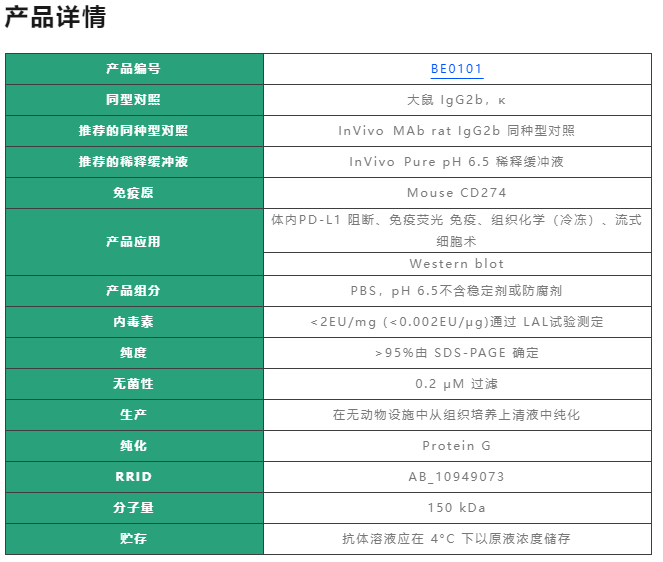
产品介绍
PD-L1 是一种 40 kDa I 型跨膜蛋白,属于 Ig 超家族的 B7 家族。PD-L1 在 T 淋巴细胞、B 淋巴细胞、NK 细胞、树突状细胞以及 IFNγ 刺激的单核细胞、上皮细胞和内皮细胞上表达。PD-L1 与其受体 PD-1 结合,PD-1 存在于 CD4 和 CD8 胸腺细胞以及活化的 T 和 B 淋巴细胞和骨髓细胞上。PD-L1 与 PD-1 的结合导致 TCR 介导的 T 细胞增殖和细胞因子产生的抑制。PD-L1被认为在肿瘤免疫逃避中发挥重要作用。诱导的 PD-L1 表达在许多肿瘤中很常见,并导致肿瘤细胞对 CD8 T 细胞介导的裂解的抵抗力增加。在黑色素瘤小鼠模型中,通过使用阻断 PD-L1 和 PD-1 之间相互作用的抗体进行治疗,可以暂时抑制肿瘤生长。10F.9G2 抗体已显示可阻断 PD-L1 和 PD-1 之间以及 PD-L1 和 B7-1 (CD80) 之间的相互作用。

已发表文献
|
用途 |
已发表文献 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Grasselly, C., et al. (2018). "The Antitumor Activity of Combinations of Cytotoxic Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Is Model-Dependent" Front Immunol 9: 2100 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Stathopoulou, C., et al. (2018). "PD-1 Inhibitory Receptor Downregulates Asparaginyl Endopeptidase and Maintains Foxp3 Transcription Factor Stability in Induced Regulatory T Cells" Immunity 49(2): 247-263 e247 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Aloulou, M., et al. (2016). "Follicular regulatory T cells can be specific for the immunizing antigen and derive from naive T cells" Nat Commun 7: 10579 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Ngiow, S. F., et al. (2015). "A Threshold Level of Intratumor CD8+ T-cell PD1 Expression Dictates Therapeutic Response to Anti-PD1" Cancer Res 75(18): 3800-3811 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Jaworska, K., et al. (2015). "Both PD-1 ligands protect the kidney from ischemia reperfusion injury" J Immunol 194(1): 325-333 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Kim, J., et al. (2015). "Memory programming in CD8(+) T-cell differentiation is intrinsic and is not determined by CD4 help" Nat Commun 6: 7994 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Zander, R. A., et al. (2015). "PD-1 Co-inhibitory and OX40 Co-stimulatory Crosstalk Regulates Helper T Cell Differentiation and Anti-Plasmodium Humoral Immunity" Cell Host Microbe 17(5): 628-641 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Tkachev, V., et al. (2015). "Programmed death-1 controls T cell survival by regulating oxidative metabolism" J Immunol 194(12): 5789-5800 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Twyman-Saint Victor, C., et al. (2015). "Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer" Nature 520(7547): 373-377 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Rutigliano, J. A., et al. (2014). "Highly pathological influenza A virus infection is associated with augmented expression of PD-1 by functionally compromised virus-specific CD8+ T cells" J Virol 88(3): 1636-1651 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Yang, X., et al. (2014). "Targeting the tumor microenvironment with interferon-beta bridges innate and adaptive immune responses" Cancer Cell 25(1): 37-48. |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Dolina, J. S., et al. (2014). "Liver-primed CD8+ T cells suppress antiviral adaptive immunity through galectin-9-independent T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin 3 engagement of high-mobility group box 1 in mice" Hepatology 59(4): 1351-1365 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Deng, L., et al. (2014). "Irradiation and anti-PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice" J Clin Invest 124(2): 687-695 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Dietze, K. K., et al. (2013). "Combining regulatory T cell depletion and inhibitory receptor blockade improves reactivation of exhausted virus-specific CD8+ T cells and efficiently reduces chronic retroviral loads" PLoS Pathog 9(12): e1003798 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Willimsky, G., et al. (2013). "Virus-induced hepatocellular carcinomas cause antigen-specific local tolerance" J Clin Invest 123(3): 1032-1043 |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Hafalla, J. C., et al. (2012). "The CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathways independently regulate host resistance to Plasmodium-induced acute immune pathology" PLoS Pathog 8(2): e1002504. |
|
in vivo PD-L1 blockade |
Zhang, L., et al. (2009). "PD-1/PD-L1 interactions inhibit antitumor immune responses in a murine acute myeloid leukemia model" Blood 114(8): 1545-1552. |
来源于优宁维药物研发官网

